HIIT training – what is it and who can benefit? HIIT is not just for weight loss!
In recent years, HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) has gained huge popularity in the fitness and sports world. And for good reason – this type of workout delivers spectacular results, both in terms of fat burning and improving overall endurance. What exactly hides behind the acronym HIIT, what benefits does it offer, and who can take advantage of it?
What is HIIT training?
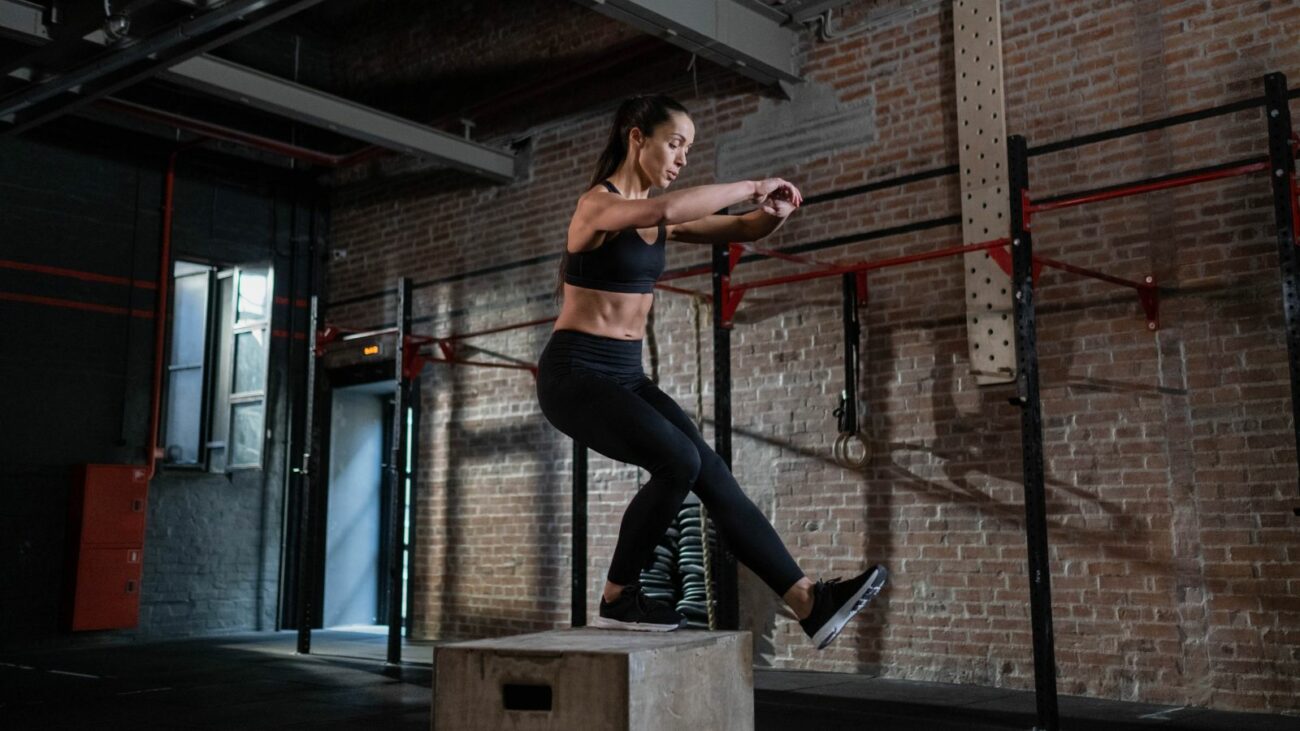
HIIT is a form of interval training where periods of intense effort are alternated with short periods of rest or low-intensity activity. The hallmark of this type of training is performing exercises at maximum effort, which allows you to maximize results in a relatively short amount of time.
Example structure of a HIIT workout:
- 30 seconds of sprinting at full intensity
- 15 seconds of jogging or walking
- repeat this sequence for 15–20 minutes
HIIT can be adapted to different forms of activity, such as running, cycling, jump rope or strength exercises, which makes it extremely versatile.
How does HIIT work?
During intense intervals, the body works in an anaerobic mode, which causes rapid burning of glycogen in the muscles. Due to the high energy demand, muscles draw energy mainly from anaerobic processes such as glycolysis. This produces lactic acid (lactate), which accumulates in the muscles and causes fatigue. In response, the body adapts by increasing tolerance to lactate and improving its ability to remove it more quickly.
After finishing the workout, the EPOC process (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption) is triggered. During this time, the body replenishes energy stores, removes lactate from the bloodstream, and restores glycogen levels in muscles and the liver. In addition, the heart and lungs work harder to deliver oxygen to tissues, which improves their efficiency.
Processes occurring in the body during and after HIIT:
- Cardiovascular system: Increased heart rate during intervals improves cardiac performance, strengthens the heart muscle and increases stroke volume.
- Lungs: Increased ventilation during effort boosts gas exchange, gradually improving oxygen uptake efficiency.
- Muscles: Microdamage to muscle fibres leads to adaptation, increasing their strength and endurance.
- Metabolism: Elevated resting metabolic rate (RMR) after training causes more calories to be burned for hours.
Benefits of HIIT
HIIT has many advantages that make it attractive for both beginners and advanced athletes.
Time efficiency
HIIT makes it possible to achieve results in a short time. Just 20–30 minutes can deliver better outcomes than an hour of traditional cardio.
Calorie burning and fat reduction
During HIIT you burn a lot of calories, and the afterburn effect continues long after the workout. It is ideal for people wanting to lose weight.
Improved endurance
Regular HIIT sessions increase lung capacity, strengthen the heart and circulatory system, and improve performance in other activities.
No monotony
The varied pace and exercises make HIIT engaging, unlike classic cardio workouts.
Minimal equipment
You don’t need specialist equipment for HIIT. You can do it at home, at the gym, or outdoors, making it highly flexible.
HIIT – not just for weight loss
Although HIIT is often associated with fat burning, it has much broader applications:
- Improved aerobic and anaerobic capacity: Increases VO₂ max, which is crucial for endurance athletes.
- Building strength and muscle endurance: Adding strength exercises to HIIT helps strengthen muscles while boosting endurance.
- Impact on metabolic health: Improves insulin sensitivity, which is important for people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Stress reduction and better mood: Intense exercise releases endorphins, which reduce stress and improve well-being.
Who is HIIT for?
HIIT is a workout that can benefit almost everyone, but there are certain groups who may especially profit from it. It is perfect for busy people who don’t have time for long training sessions. HIIT usually lasts 20–30 minutes, making it an ideal solution for those with tight schedules.
Athletes also often turn to HIIT, as its intensity and variability improve both aerobic and anaerobic performance, which is very useful in endurance and strength sports. Thanks to its high calorie burn, people with excess weight may see quick results in weight loss.
It is also a great option for fans of dynamic and challenging workouts. With its variety of exercises and changing tempo, HIIT provides both challenges and satisfaction, making it attractive for people looking for demanding training experiences.
How to start HIIT training?
If you’re just starting your HIIT journey, remember a few rules:
- Warm-up – always start with 5–10 minutes of warm-up to prepare your body for intense effort.
- Adjust intensity – choose exercises and pace suitable for your fitness level.
- Progression – gradually increase intensity or the number of intervals to keep challenging your body.
- Recovery – allow a rest day between HIIT workouts to avoid overtraining.
Sample HIIT workout for beginners
Duration: 20 minutes
Equipment: none (mat optional)
- 30 seconds: jumping jacks at maximum intensity
- 15 seconds: rest or march in place
- 30 seconds: burpees
- 15 seconds: rest
- 30 seconds: squat jumps
- 15 seconds: rest
Repeat the entire cycle 4 times.
Summary
HIIT is an extremely effective form of training that benefits those aiming to lose fat as well as those who want to improve endurance or strengthen muscles. Thanks to its universality and time efficiency, HIIT works for a wide range of people, from beginners to advanced athletes.
Start with short sessions, pay attention to your body, and enjoy the benefits HIIT brings!